Clustering
If you wish to run the same website concurrently on multiple hosts you can use the Pack or Cluster module.
The Web Cluster module uses Rsync to get all files to all servers.
The Web Pack module shares files to all servers via an NFS mount. The NFS setup must be done manually.
Using the Pack module
If you wish to run the same website concurrently on multiple hosts you use the Pack module. Enable the pack module as you would any other drupal module.
A Pack consists of a single server node that is specified as "pack" and any number of server nodes specified as "apache" or "nginx". Aegir rsync's configuration (Apache & Nginx) to "all" nodes in the Pack and rysnc's the platform and site code to only the "master" node in the Pack. All other "slave" nodes will see the platform and site code via NFS.
Configuring the Pack server node:
The "pack" server node will not be used by Aegir to physically deploy sites or platforms on, so consider it more of a 'virtual server group' for logistical purposes only. When creating the pack node, you do not need to supply a valid Server hostname or IP address, so choose a naming convention that makes sense in your environment.
Next, select the "pack" radio button option under the web configuration when creating or editing the server node, in order to designate this server node as the "pack" server.
Now select the "Master" server from the list of Master servers. The Master server will be the server node that Aegir rsync's the platform and site to. Typically, you would choose the Aegir server itself as the 'master'.
Finally, select the "Slave" servers from the list of Slave servers. The Slave servers will have the Apache or Nginx config rsync'd to them but not the platform or site code, since those will be available to all Slave servers via the NFS share.
Configuring the Web server nodes:
Configure all web server nodes using these instructions. Take care to ensure the 'aegir' user and group on your NFS client machines, have the same UID/GID as that of the NFS server, or else you may run into permissions issues with NFS.
Then mount the files on the remote server.
On the NFS server:
sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server
echo "/var/aegir/platforms 10.0.0.0/24(rw,no_subtree_check)" >> /etc/exports
sudo service nfs-kernel-server reload
(Replace the subnet here or add specific /32 hosts as necessary for your environment)
Then on the web servers (Master, if it wasn't also the NFS server, and the Slaves):
sudo apt-get install nfs-client
sudo mount 10.0.0.1:/var/aegir/platforms /var/aegir/platforms
(Replace the NFS server's IP here with that of your master server/Aegir server)
Add this to your fstab on the servers that mount the NFS share, so that the share is mounted on boot:
10.0.0.1:/var/aegir/platforms /var/aegir/platforms nfs rw 0 0
Creating a Platform on a Pack:
When configuring a Platform to be deployed on a Pack, choose the "Pack" server node from the Web server radio group during the Platform node creation. Then you choose this Platform as usual when adding a site, and that site will be served from any servers within the Pack.
Caveats
Relying on an NFS share to serve your entire /var/aegir/platforms can be a single point of failure if the NFS share becomes unavailable. You may want to look into providing some sort of failover for NFS (google for things like DRBD and Heartbeat), or using some other form of redundancy for your NFS (Netapp filer clusters etc)
Below is an example diagram of a Pack cluster known to be functioning in production (with an optional MySQL-MMM cluster out of scope for this documentation), which may help you visualise the Pack and how it can be put together.
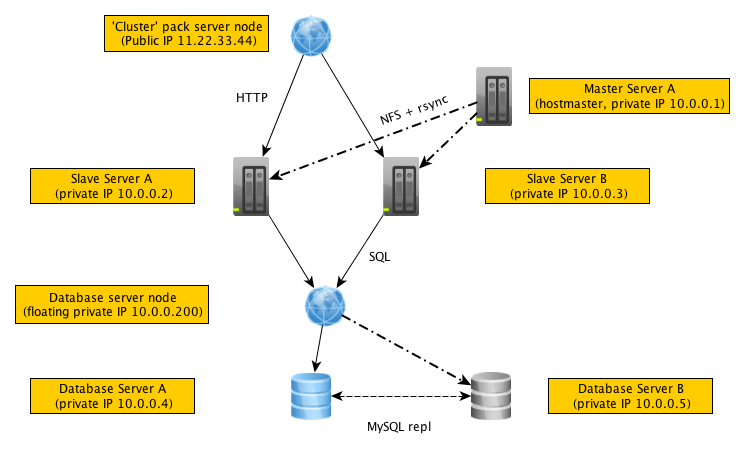
Using the Cluster module
This documentation page is about the Web Cluster module.
Setting up Web Clusters
In this setup, we will add two web servers and a single database server.
- Under Admin > Hosting > Features, enable the "Web Clusters" module.
- Setup two or more additional Remote Servers using the Remote Server Instructions.
- Create Remote Server Nodes: Visit Servers > Add Server and enter the hostname of your remote server. For Web Server, select Apache, Apache SSL, NGINX, or NGINX SSL.
- Repeat Step 3 for all of your web servers.
- Create Cluster Server Node: Visit Servers > Add Server and enter any hostname (something like "cluster" so you can identify it.). For Web Server, select Cluster and select all of the web servers you wish to add to the cluster.
- Setup Database Server: You have two options here.
- Provision a new, separate database server using only the MySQL section above. Then visit Servers > Add Server, enter the new server's hostname, and select "MySQL" for "Database" and enter the root username and password you set during the Remote Server Instructions.
- Use an existing server other than "localhost". Aegir installs a database server called "localhost" by default. You cannot use this server for sites installed on remote servesr. Find the default web server aegir installed (named after the hostmaster hostname). Click Edit, then select "MySQL" for "Database" and enter the root username and password. If you use the server with the same hostname as the "localhost" database server, you can use the same root username and password.
- Make sure the Database Server Hostname resolves to the database server IP. This can be done with DNS or by manually editing the /etc/hosts file on the remote servers.
- Create or Edit a platform node, and select the cluster server you created in step 5.
- Create a site node, and select the database server you created in step 6.
If all goes well, the site should install.
To test that the site is available from both servers, you must edit your DNS or hosts file:
- Given your site node URL is myclustersite.com, edit /etc/hosts or your DNS so myclustersite.com resolves to the IP of remote server #1.
- Visit the URL http://myclustersite.com in the browser. If the site works, we know we can load the site from remote server #1.
- Edit /etc/hosts or your DNS so myclustersite.com resolves to the IP of server #2.
- Visit the URL http://myclustersite.com again. If the site works, we know we can load the site from remote server #2.
Final Tasks
There are two important final tasks to get a working drupal site running on a server cluster:
-
Load Balancer. Now you must setup a load balancer that will route requests to both remote server #1 and #2.
-
Shared Files folder. Uploaded files will only go to one server when you upload them. They will appear as missing when requests come in to the other servers.
There are a number of ways to deal with this: You can use NFS to create a shared files folder, or you can configure your load balancer to always send requests for the files folder to a single server.
Setting up a load balancer and dealing with the files folder is out of scope of this article, for now.